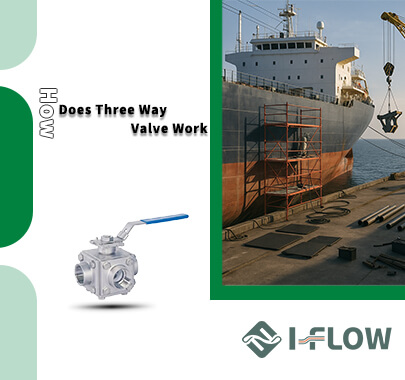
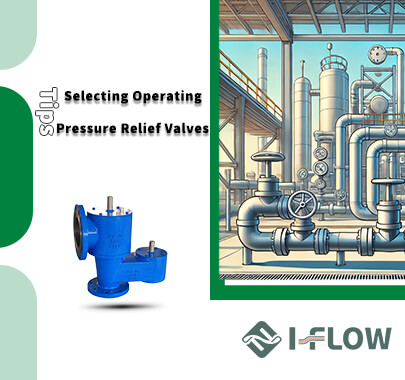
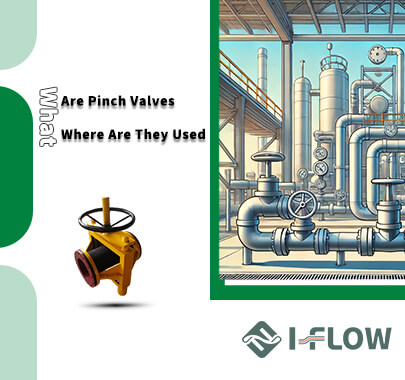
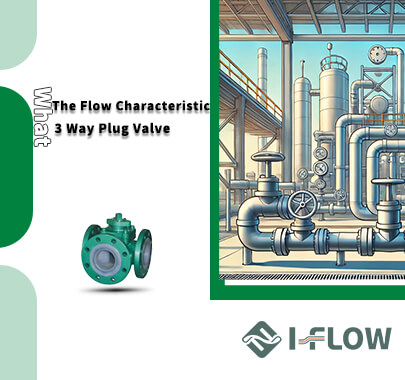
- HOME
-
PRODUCTS
We offer highly cost-effective products and professional after-sale service for the marine, HVAC, water, oil & gas, fire fighting industries. Our valves, all delivered by experienced technicians, are of guaranteed good quality.
> Water > HVAC > Marine > Oil & Gas > Industry > Fire Fighting -
ABOUT
With years of experience, I-FLOW knows the market very well. We can provide excellent one-stop solutions for our clients. For more information about our valves and service, contact us today!
> CEO'S Greeting > Our factory > Career & culture > Fairs and events -
QUALITY
I-FLOW has an excellent R&D team. Managed strictly under ISO 9001, we inspect and test each of our valves to make sure 100% qualified.
> Research & Development > Quality Control > Quality Assurance > Certificates -
APPLICATIONS
We, together with our associated companies, have obtained various types of certificates, including CE, WRAS, DNV, GL, LR, ABS etc. I-Flow valves are now widely used all over the world, in Shangrila Hotel, Kerry Center, Milan Expo, Fiat Workshop, IKEA, COSCO vessels, etc.
> Marine > HVAC > Water Treatment > Oil & Gas -
NEWS
Accumulating 10 years' experience in valves, we are an excellent solution provider. Keep in touch now and experience how your needs are well addressed.
> Client Stories > Our Projects > Company News > Industry News -
CUSTOMER SERVICE
With over 10 years of experience in the industry of valves, I-FLOW will provide the perfect solution for your project. Contact us now, we will solve all your problems.
> Download > After-sale Service > FAQs - CONTACT

.png)
 en |
en |